What is the best internet in Australia?
Are you moving to a new house? How can you get the best internet connection? An internet provider may offer NBN. However, faster technologies for the same price, such as wireless 4G or 5G, might be available at your location.
Here is a comparison of the internet technologies in Australia.
| technology | download / upload / ping | average plan price |
|---|---|---|
| NBN | 25 - 100Mbs / 18Mbs / 5ms | $85 Unlimited |
| NBN Ultrafast | 250 - 600Mbs / 40Mbs / 5ms | $100 Unlimited |
| 5G home | 300Mbs / 20Mbs / 15ms | $89 Unlimited from Optus |
| Cable | 120Mbs / 3Mbs / 10ms | $70 Unlimited, phased out |
| ADSL | 24Mbs / 1Mbs / 20ms | $30 Unlimited, phased out |
| retrieved on Nov 2024 | ||
Those are maximum NBN speeds within a few hundred metres of the exchange or fibre node. Actual internet speed varies depending on your location, the quality of the phone wiring in the house or the WiFi setup.
NBN comparison
The table below shows the most and least expensive selection of NBN providers as of Nov 2024. Prices and speeds are estimates and may vary depending on specials. Several dozen other providers offer deals that fall within similar price ranges.
| Provider | Slow | Medium | Ultra fast |
|---|---|---|---|
| Telstra | $89 | $115 | $150 |
| Optus | $75 | $109 | $129 |
| iinet | $70 | $85 | $100 |
| TPG | $75 | $80 | $105 |
| Dodo | $59 | $84 | $100 |
| Exetel | $64 | $80 | $100 |
| Belong | $70 | $85 | N/A |
| Flip | $53 | $74 | $95 |
The NBN speed tiers in the table: Slow: Speeds capped to below 25Mbs.Medium: Speeds around 50Mbs.Ultrafast: Speeds 250Mbs - 800Mbs.
Telstra has the highest prices among the NBN providers in Australia, while Flip, a new provider based in Maroubra, offers some of the lowest rates. However, service quality can differ based on location and setup. Before choosing a provider, please do your research and, at the very least, verify that their support phone number is attended.
What is the best internet in my area?
It is a matter of priorities. Price-wise and speed, 5G is the best for home if available. Also, you can get 5G and 4G on the same day by purchasing them at the ISP shop. However, NBN is the only option if your security system or business VPN router requires a fixed IP address. Ultrafast NBN with speeds up to 1000Mbs and over is available in some locations.
There are cheap NBN plans from $40, with a caped speed of only 15Mbs or less, sufficient for essential internet and TV.
Typically, speeds are around 50Mbs. However, when opting for higher speeds, ISPs cannot guarantee the exact speed until after installation due to variations at the specific location. You can check your address on the internet provider's website or ask your neighbours. Nevertheless, actual connection speeds can differ from expectations.
NBN
Check the address on the NBN website. If NBN is available, you can choose an NBN provider to your liking.
What is the best NBN internet provider in my area?
Most NBN providers don't own the hardware but differ in their service. Some offer fast internet routing. Others save costs by using slower routes. Due to the internet's complexity and local laws, many ISPs aren't transparent about their exact offerings.
Wireless
Whether using 4G or 5G, it utilizes the same technology as your mobile phone with the same SIM card. The only difference is the wireless modem, usually combined with the router. However, you can also use a mobile phone as a modem. Wireless technology and prices are constantly improving. For instance, in Nov 2023, Optus offered a 220GB data SIM-only plan for just $69 per month. Unless you and your family constantly stream 4K movies, that should be sufficient for work and leisure.
One downside of wireless is the lag and stability in remote areas. Depending on your proximity to the network tower, the lag can exceed 30ms compared to 5ms over fixed NBN. Lag and jitter can introduce noticeable delays and inconsistencies while browsing the internet despite downloading speeds exceeding 100Mbps. However, this is generally fine in urban areas where mobile towers are typically nearby. 5G connection speed near the tower can be up to 1000Mbs with a ping of 5ms.
How can I check what 4 - 5G speed I can get in my location?
Do a speed test on your mobile phone. Because the 4G - 5G internet uses the same technology, it will be at least as fast as the mobile phone at the exact location, assuming the 4G internet and mobile phone provider are the same.
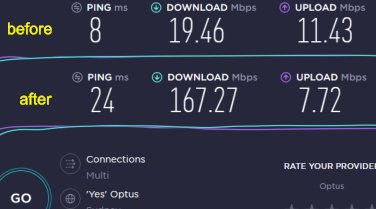 NBN changed to Optus 4G at Avalon
NBN changed to Optus 4G at Avalon
Is NBN the same as cable?
If your home was previously connected to Optus Foxtel TV or the internet via coaxial cable, that cable may be used for NBN HFC Hybrid Fibre Coaxial. It has higher speeds and better lag than traditional cable internet and is slightly better than NBN over copper phone lines.
| Feature | Old Optus/Foxtel Cable | NBN HFC Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Download Speed | Up to 100 Mbps | Up to 1 Gbps |
| Upload Speed | 2-8 Mbps | 15-100Mbps |
| Latency | 10-30ms | 5-10ms |
Whether NBN runs over cable or phone lines is planned upfront, but sometimes you may have a choice. You can check the type of NBN connection available at your address on your ISP's website.
Apart from NBN over coaxial cable, there are two other ways NBN can be delivered to your home: FTTN, which uses existing copper phone lines, and FTTP, which requires the installation of new fibre cables. The installation method is dictated by your NBN provider and the plan you opt for. For plans with speeds under 100 Mbps, the end user generally won't see the difference between these technologies. If you're considering upgrading to super fast internet speeds up to 1Gbps, provided it's available in your location, upgrading to FTTP might be necessary.
Problems with coaxial cables
Cables are not always connected to the internet provider. Occasionally, builders incorporate coax cables in the house design, but the internet provider won't connect a new home to the network for a reasonable price. Coax cables are also used for Foxtel satellite dishes or free-to-air TV antennas unrelated to the internet.
ADSL
If NBN and cable are not available, the ADSL might still be. The copper phone line can be 50 years old, hence the slow internet speed. ADSL speeds can exceed 20Mbs but are usually around 10Mbs. NBN is times faster than ADSL was on the same line. ADSL plans are still available from some ISPs for around $50 per month. ADSL lag is usually around 6ms, and stability is excellent, making it a good budget option for some locations.
How do I check what ADSL speed can I get at my location?
ADSL internet speed hugely depends on proximity from the phone exchange. You can google 'DSLAM map' to see the distance from the exchange to your house and maximum ADSL speed. The best map is provided by TPG. ADSL from other providers will give the same speed because lines and phone exchanges (where nodes are) are the same for all internet providers.
Internet connection quality parameters
Download speed
Internet download speed is vital for fast file downloads to your device but doesn't solely determine website loading speed. Other factors also influence how quickly websites load.
Upload speed
The upload speed tells how fast you upload information to the internet. Good upload speed is needed when you upload large files such as PDFs to the cloud or videos to YouTube. Browsing web pages, such as Facebook or using mobile applications, depends on upload, albeit not as much as a download. Unfortunately, internet providers do not advertise upload speed. The hardware or network protocols often limit Upload speed. For example, cable internet was limited by 3Mbs uploads even though the download speed may be higher than 100Mbs. That is why uploading video to YouTube from a mobile phone on 4G could be ten times faster than on WiFi.
Network latency
Latency is the time it takes for a resource to load, such as a webpage or separate elements, pictures and other files. This delay is measured in milliseconds (ms). Latency is influenced by several factors, including the physical distance between the sender and receiver, the quality and capacity of the network infrastructure, the number of network devices the data must pass through, and the processing time at each network device and computer.
The ping
A ping is a tool or command used to measure latency. When you run a ping command, your device sends a small packet of data (ICMP echo request) to a specific server or IP address. The server then responds with the same packet (ICMP echo reply). The time it takes for this round-trip communication to occur is known as the ping time.
Ping vs Latency
Ping measures the delay of a standard packet, while latency is a broader parameter requiring a definition of what is measured. The lesser the ping and latency, the better.
Jul 2019 updated Oct 2023 Tags: WiFi